GitHub
This section explains how to integrate your SCM with GitHub using StackSpot Workflow.
Connecting your
Currently, StackSpot supports five possible workflows:
- Application creation
- Infrastructure creation
- Plugin application
- Action execution
- Workflow execution
Prerequisites
1. Have a repository for your pipelines
Before integrating SCM with StackSpot, make sure you have a dedicated repository in your organization for pipelines. Once you set it up, you can trigger them remotely via API, providing the required input data for each workflow.
You can use an existing repository or create a new one. Learn how to create a repository on GitHub.
2. Generate a Personal Access Token on GitHub
- You need write permission on the Workflow repository to continue.
For security purposes, credentials such as the Personal Access Token (PAT) are stored in an encrypted format on StackSpot. Once saved, this information cannot be viewed or retrieved through the platform.
- Log in to your GitHub account.
- Click your profile picture and select 'Settings'.
- In the main menu, scroll down and click 'Developer Settings'.
- Click 'Personal Access Tokens', then select 'Tokens Classic'.
- Click 'Generate new Token' and choose 'Generate new Token (classic)'.
- In the "New personal access token (classic)" form, fill in the 'Note' field with a description for the token. Set an expiration date in the "Expiration" field.
- Under "Select scopes", check the following boxes:
- All "repo" options:
- repo:statusAccess
- repo_deployment
- public_repo
- repo:invite
- security_events
- "workflow"
- "write:packages"
See the example below:
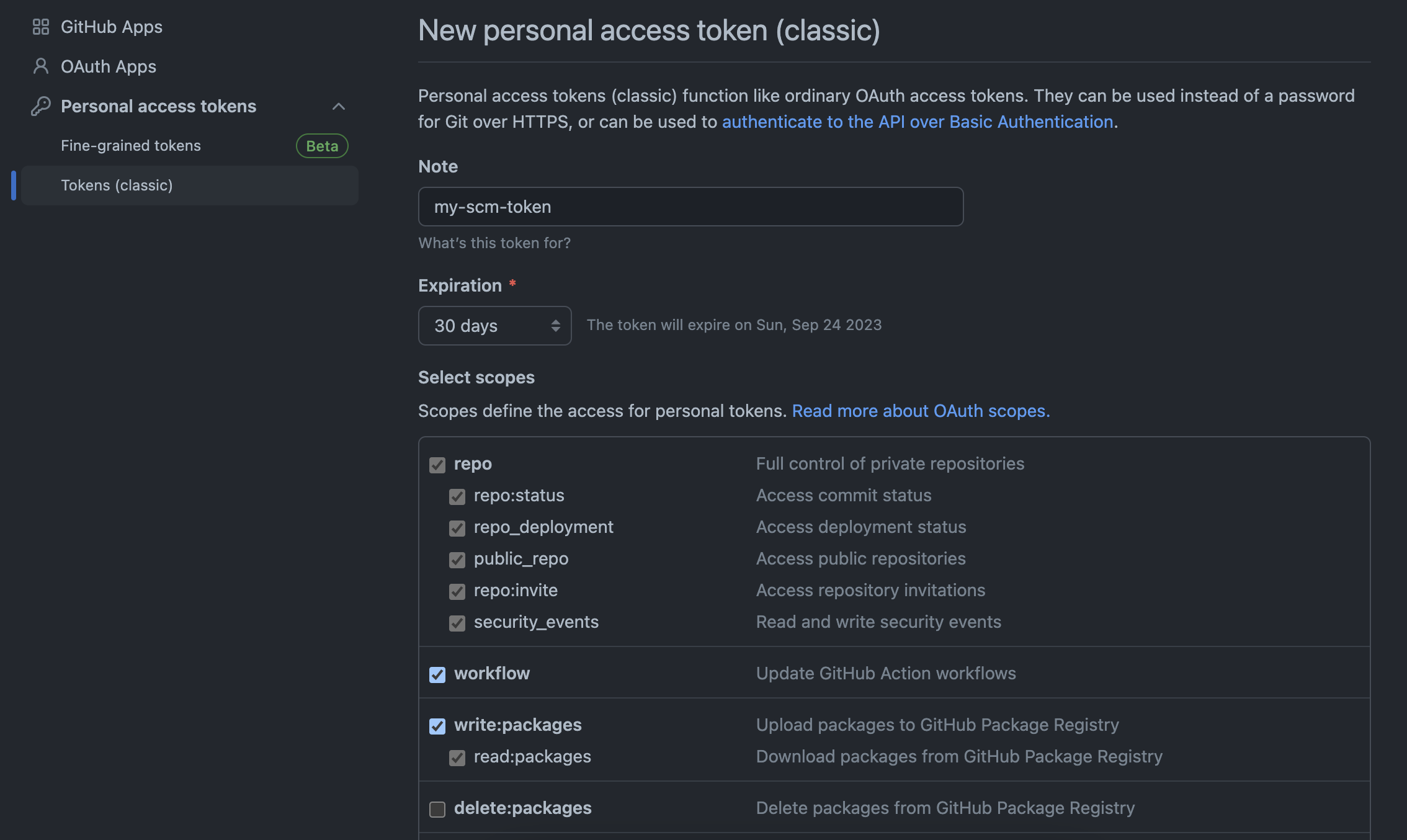
The required scopes depend on your company's needs. Select all that apply to your use case.
-
Click 'Generate Token' at the bottom of the page. Copy and save the generated token immediately, as it will only be shown once.
-
(Optional) If your organization uses SSO (Single Sign On), authorize your token:
- In GitHub, go to 'Settings' > 'Developer Settings' > 'Personal access tokens (classic)', find your token, and click 'Configure SSO':
The gifs/images are an example, search for the name of your Organization in the GitHub.
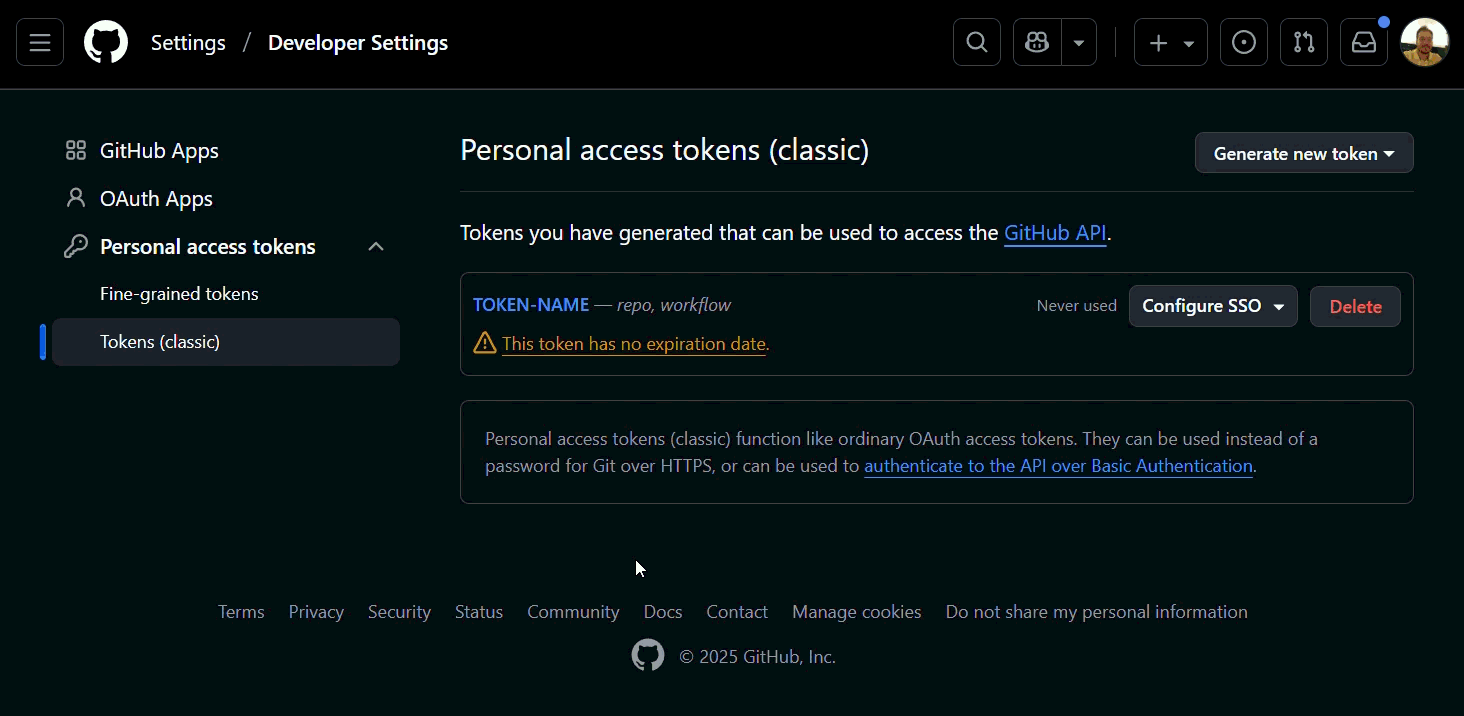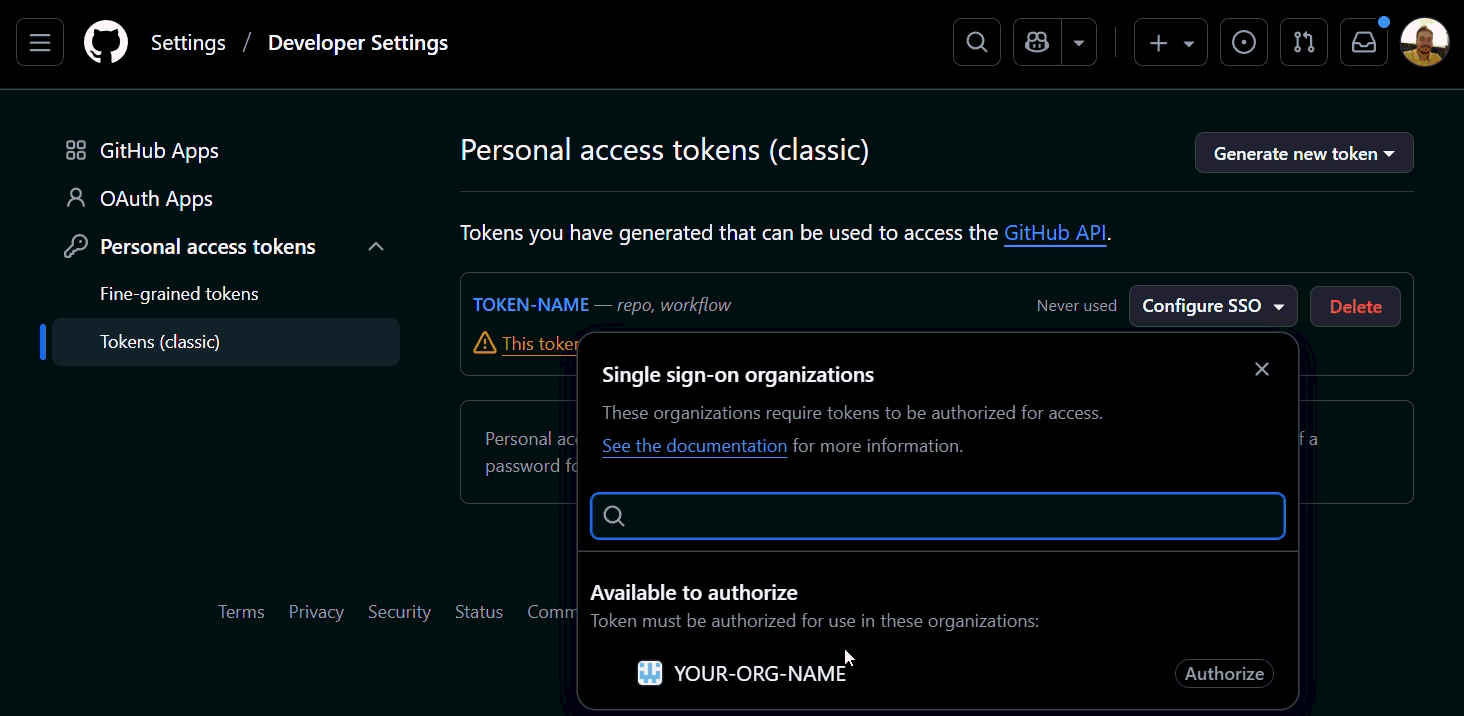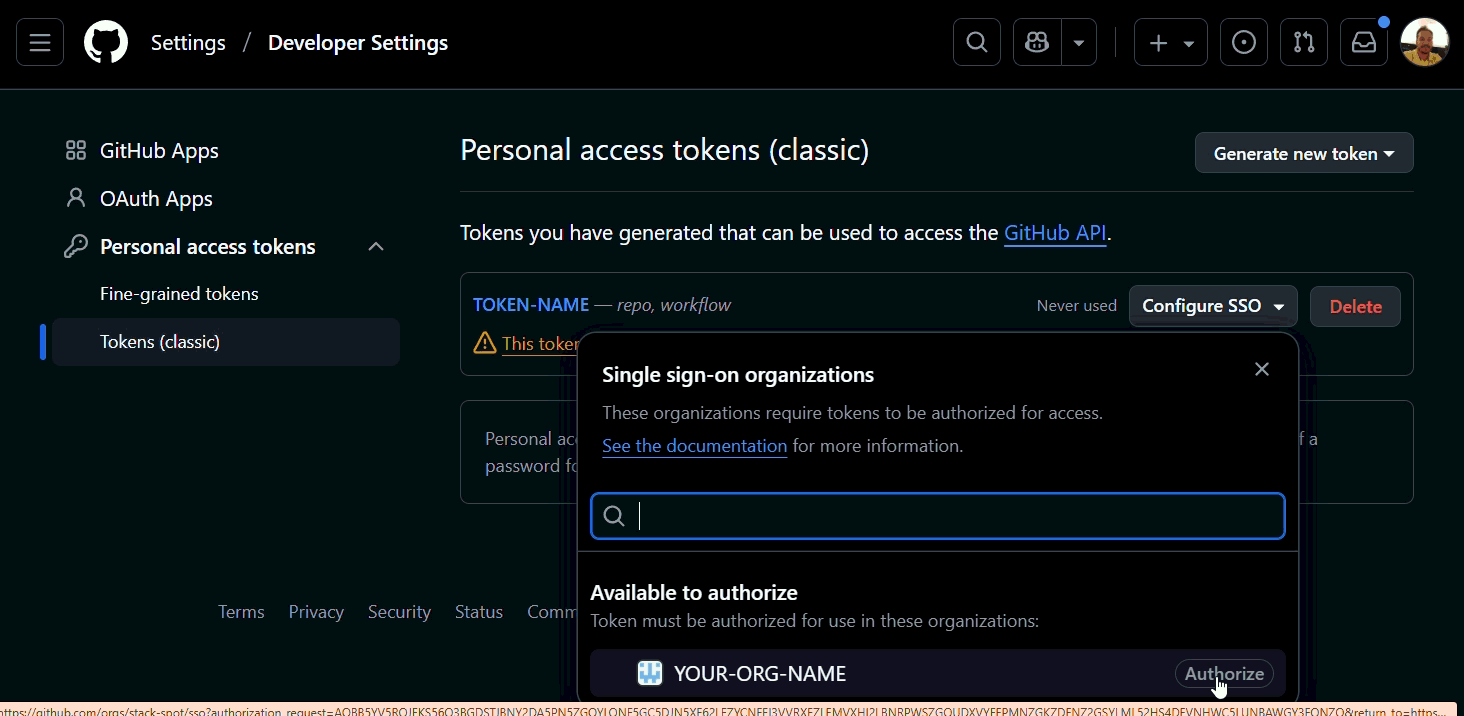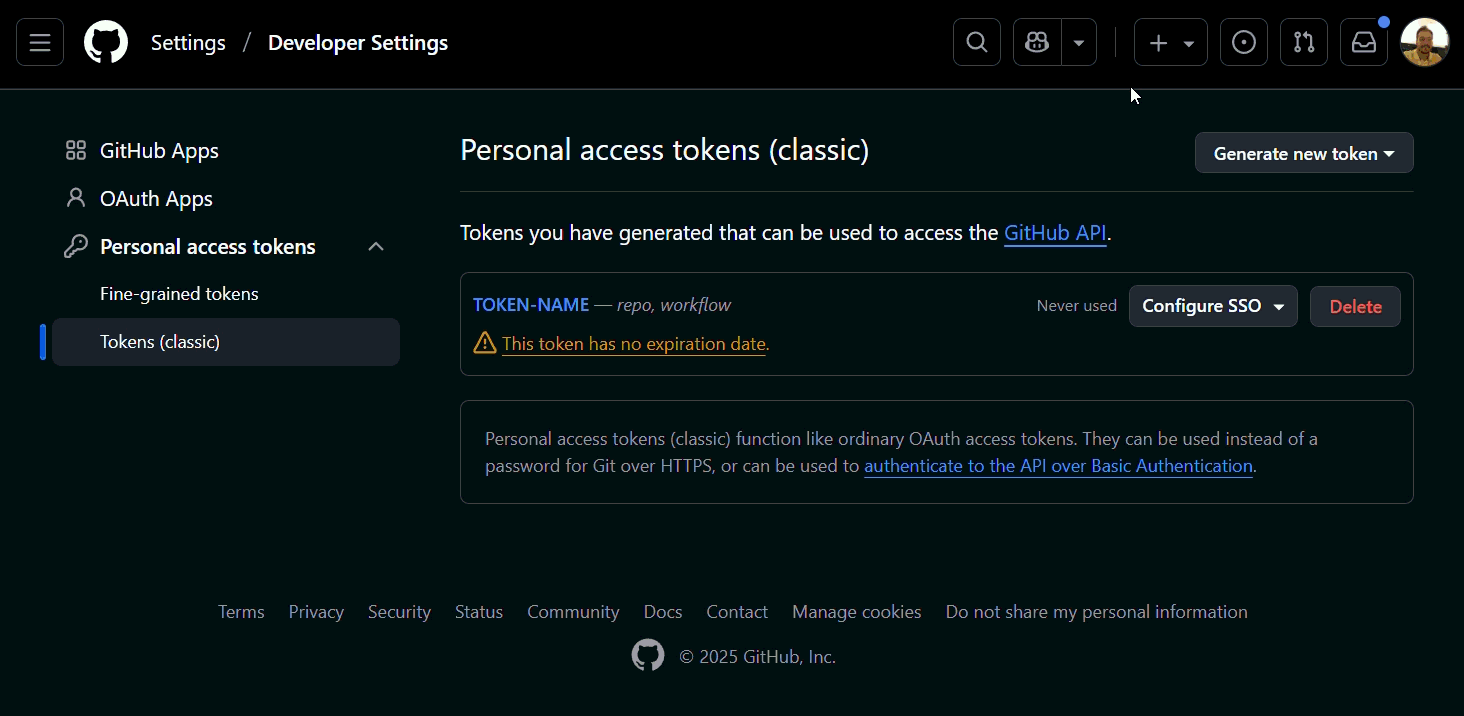
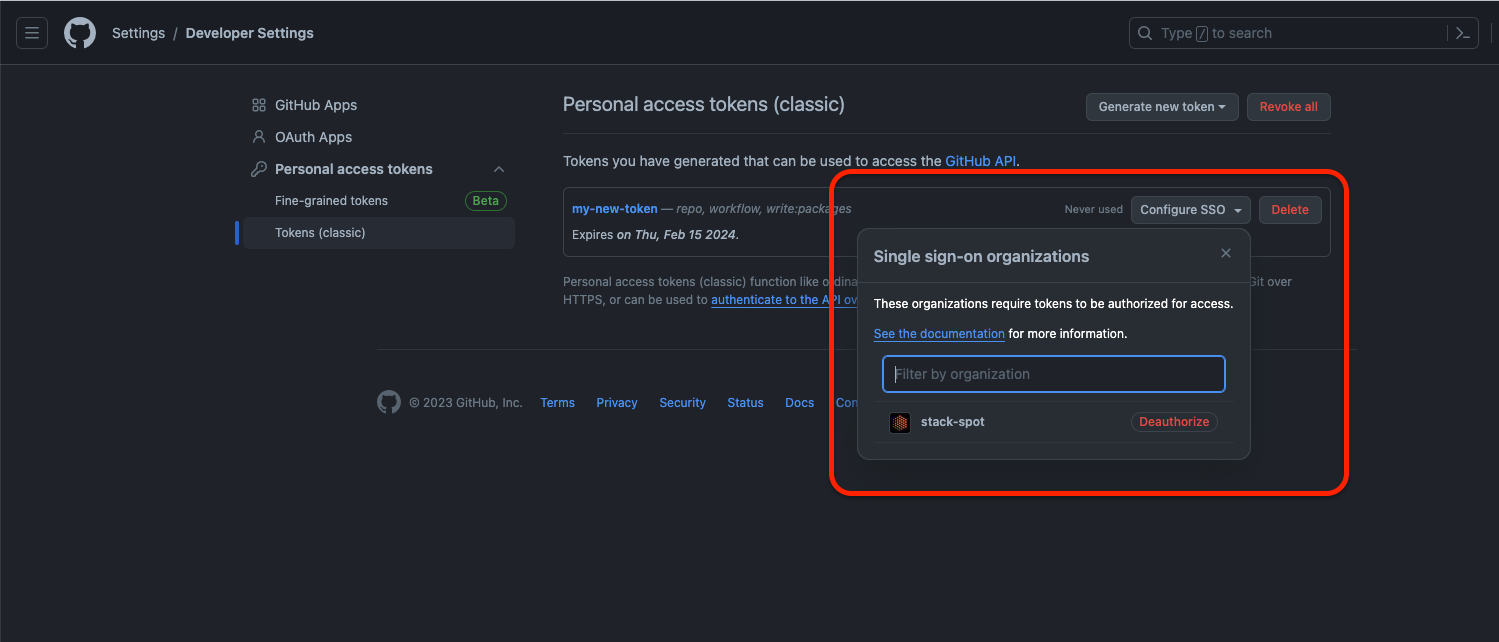
Check if your token is authorized. See an example below:
For more details, see the GitHub documentation.
Automatically configure pipelines (Recommended)
Run the following steps using the STK CLI. Make sure you have already created a repository. Learn how to create a repository on GitHub.
Step 1. Run these commands:
- If you are in an active Workspace, exit it:
stk exit workspace
- After exiting the Workspace, run the Workflow:
stk run workflow stackspot-core/stackspot-setup-scm@3
Step 2. When prompted, select GitHub as your SCM provider.
Step 3. Answer the following questions:
- Organization name: Enter your GitHub username.
- Repository Name: Enter the name of the repository you created for StackSpot Workflows.
- Personal Access Token: Enter the token you generated earlier.
- The repository to setup scm already exists? (Y/n): Type 'Y' if the repository exists, or 'n' if it does not.
- Want to do the setup in main branch or create a pull request? (Y/n): Type 'Y' to create a pull request and specify the target branch, or 'n' to keep the configuration in the 'main' branch.
The token user and the Personal Access Token must have write permission on the organization repository. If the repository does not exist, you must have permission to create repositories.
In some SCMs, Project Name and Repository Name mean the same thing. You can identify these fields in the URL:
https://github.com/[GITHUB-USERNAME]/[REPOSITORY-NAME]
Example:
https://github.com/stack-spot/stackspot-workflows-action
For more information, see the GitHub documentation.
This is not the Portal's Personal Access Token.
- Create a repository: If the Action does not find a repository, you will be prompted to create one. Choose Yes to create a new repository. If you choose No, the Action will stop.
Check your repository on GitHub under Actions. You should see the "StackSpot workflow dispatch" configured.
You will also find the Webhook already set up in your project's GitHub settings.
If the setup was successful, proceed to integrate GitHub with your StackSpot account. If you could not complete the automatic setup, follow the manual steps below:
Manually create the repository and pipelines
Step 1. In your terminal, using STK CLI, run:
mkdir <repo-name>
cd <repo-name>
mkdir .github
cd .github
mkdir workflows
Example:
mkdir repo-runner-actions
cd repo-runner-actions
mkdir .github
cd .github
mkdir workflows
Step 2. Create a file named "stackspot.yml" in ".github/workflows" with the following content:
name: Stackspot resume workflow
on:
workflow_dispatch:
inputs:
workflow_execution_id:
type: text
required: true
workflow_inputs:
type: text
required: false
jobs:
run:
name: Run workflow
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
env:
LANG: C.UTF-8
LANGUAGE: C.UTF-8
LC_ALL: C.UTF-8
PYTHONIOENCODING: utf-8
HTTP_ENABLE_DEBUG: false
steps:
- name: "[StackSpot] Install CLI"
run: |
cd /tmp
curl -fsSL https://stk.stackspot.com/install.sh | bash
echo "~/.stk/bin" >> $GITHUB_PATH
stk --version
stk upgrade
- name: "[StackSpot] Login"
run: |
stk login -id ${{ secrets.STK_CLIENT_ID }} -key ${{ secrets.STK_CLIENT_KEY }} -r ${{ vars.STK_REALM }}
- name: "[StackSpot] run workflow"
run: |
stk resume workflow ${{ inputs.workflow_execution_id }}
Step 3. Commit your changes:
git init
git remote add origin https://github.com/<github-username>/<repository-name>.git
git add .
git commit -m "Setup Runner"
git push
Example:
git init
git remote add origin https://github.com/my-username/repo-runner-actions.git
git add .
git commit -m "Setup Runner"
git push
In some SCMs, Project Name and Repository Name mean the same thing. You can identify these fields in the URL:
https://github.com/[GITHUB-USERNAME]/[REPOSITORY-NAME]
Example:
https://github.com/stack-spot/stackspot-workflows-action
Step 4. Set up a Webhook in your repository:
- Log in to your GitHub account.
- Click your profile picture in the top right and select 'Your repositories'.
- Open the repository you created for pipelines, then go to 'Settings'.
- In the main menu, click Webhooks and then Add webhook.
- Fill in the fields as follows:
- Payload URL:
https://workflow-api.v1.stackspot.com/workflows/github/callback - Content type:
application/json - Secret: (Leave blank)
- SSL Verification: Check 'Enable SSL verification'
- Which events would you like to trigger this webhook? Select 'Let me select individual events' and check 'Workflow runs'
- Check 'Active'
- Click 'Add webhook' to finish.

If the setup was successful, proceed to integrate GitHub with your StackSpot account.
Integrate GitHub with StackSpot
Complete these steps in the StackSpot Portal.
Configure via GitHub PAT (Personal Access Token)
Step 1. Go to the Account Portal directly, or after logging in to StackSpot Portal, click your profile avatar.
Step 2. Click the 'Organization' option.
Step 3. In 'EDP' section, click the 'SCM' button.
Step 4. Click the Edit button. In Select a Provider, choose GitHub.
Step 5. For Authentication Method, select PAT (Personal Access Token) and fill in:
- User: Your GitHub username
- Token: The Personal Access Token you generated earlier
To save, click the 'Save' button.
Step 6. In Workflow settings, click the Edit button and choose how your organization will manage SCM access.
Enable or disable 'Will the organization manage SCM access via User PAT?':
- Enabled: Each user manages access to GitHub via PAT or GitHub App.
- Disabled: The company manages access to GitHub.
Step 7. In Workflow URL, enter the repository URL with the pipelines so StackSpot knows where your workflow is configured. For example: https://github.com/my-organization/repo-runner-actions.
Step 8. Review your information and click the 'Integrate with StackSpot' button.
You're all set!
Configure via GitHub App
Before you start:
You need to create a GitHub App if you don't have one yet. Learn how to create a GitHub App.
After creating the App in GitHub, grant the following permissions:
- Go to 'Settings > Developer settings > GitHub Apps'.
- Find your App and click 'Edit'.
- Click 'Permissions & events', then expand 'Repository permissions'.
- Set 'Read and write' permission for:
- Contents
- Pull requests

If your App creates workflows, set 'Read and write' for 'Workflows':

If your App needs to access Actions to manage workflows, workflow runs, or artifacts, set 'Read and write' for 'Actions':

Grant access to each resource your App needs.
After installing the App in your Account or Organization, select the repositories you want to use with StackSpot.
- In GitHub, go to 'Settings > Applications'.
- Find your App and click 'Configure'.
- Under 'Repository access', select 'Only select repositories' and choose the repositories you want to use with StackSpot.

After granting access to your App, follow these steps:
Step 1. Go to the Account Portal directly, or after logging in to StackSpot Portal, click your profile avatar.
Step 2. Click the 'Organization' option.
Step 3. In 'EDP' section, click the 'SCM' button. Then click 'Add SCM Integration'.
Step 4. In Select a provider, choose GitHub.
Step 5. For Authentication Method, select GitHub APP and fill in:
- AppID: The Application ID, e.g.,
145236. - InstallerID: The App installation ID, found at the end of the URL, e.g., URL:
https://github.com/settings/installations/88969132, so the InstallerID is88969132.
You can find all the information you need for the GitHub App fields here:
For users: Go to Settings > Applications > Your GitHub App. The data is in the main menu under: General, Permissions & Events, Install App, Advanced, and Optional features.
For organizations: Go to Settings > Installed GitHub Apps. The data is in the main menu under: General, Permissions & Events, Install App, Advanced, and Optional features.
Step 6. Upload the .pem file for the Private Key and click 'Next step'.
Step 7. In Workflow Configuration, disable 'Will the organization manage SCM access via User PAT?'.
If you enable this option, each member of your account will need to configure their own SCM Access.
Step 8. In Workflow URL, enter the repository URL with the pipelines so StackSpot knows where your workflow is configured. For example: https://github.com/my-organization/repo-runner-actions.
Step 9. Review your information and click 'Integrate with StackSpot'.
You're all set!